Are we alone? |
Definition of the life | |  Automatic translation Automatic translation | | Updated June 01, 2013 |
The magnitude of the issue does not simply respond as if there is an answer, because the question concerns both the philosophical aspect that the chemistry of life.
We observe that life evolves in the time by taking a path defined by an infinite number of parameters, which makes it unpredictable and indefinable.
Yet there is a biological definition of life: "An organism is alive when said exchange of matter and energy with its environment by maintaining its autonomy when it reproduces and evolves by natural selection."
All living organisms ensure their stability by reacting to changes in their environment.
Life has therefore a faculty of adaptability and learning. Is it not rather that life?
But we also observing galaxies, stars and planets, the material is able to self-organize without being alive. However, a good definition of life must take into account this concept, ie, the ability of the material to gradually climb the ladder of complexity.
A study funded by NASA indicates that the heavy bombardment of asteroids that took place there nearly 4 billion years ago, was not enough for sterilized Earth completely. | | The study focused on an event known as the end of bombardment (Late Heavy Bombardment) or LHB.
This event occurred about 3.9 billion years ago and lasted 20 to 200 million years. The results of their study show that while the bombing could have generated enough heat to sterilize the surface of the Earth, microbial life at the shelter in the basement would have survived anyway.
Michael H. New, astrobiologist said: "These results are important because they indicate that if life began before the LHB before 4 billion years ago, it would have survived in shelters and then be extended to fill our world."
The tenacity of life is it not proof that it is present everywhere in the universe, waiting patiently for a favorable environment to continue its path toward complexity?
It is difficult to believe that life exists only on Earth. Wherever there is liquid water, there is a possibility of life even under the icy crust of planets or satellites of planets. Life thrives in places where even the sun's energy does not penetrate, we see into the depths of our planet. We recognize life when we see it! | | 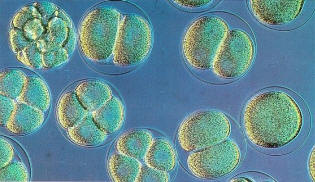 Image: Earth has certainly not the monopoly of organic molecules, those that make up living things. The building blocks of life can be hosted by celestial bodies that move in the vastness of space and deposited on a planet hospitable. If we have trouble defining 'life' when appear, we recognize. We recognize the life when we see it! |
Are we thus alone? | | | | |
As long as we did not discover an extraterrestrial life, we are effectively alone. Let us take into account the chances which we have to discover a life somewhere else. Since 1995, the astronomers began looking for exoplanets and discovered several hundreds, and it is going to accelerate. Our chances grow every day...
The physical conditions are the same everywhere in the Universe: the galaxies contain stars, stars have gaseous or / and telluric planets, planets are constituted by infinity of chemical elements as hydrogen, carbon, water...
Take only one galaxy among the billions existing, our, the Milky Way. In the Milky Way, there are 100 to 300 billion stars, what produce a considerable number of planets. Even if the necessary conditions to the emergence of the life are difficult to combine, the number of existing planets allows us to think that the life develops or develops probably somewhere else. The astronomy progresses are going to show that the favorable sites and conditions to the life are universals, and that, the chemistry of the carbon (at the origin of the life) meets itself everywhere in the Universe.
Today, we haven’t any formal proofs of this other life, but I think that it must have a large number of places where the life abounds, from the primary state to the advanced state as our and certainly beyond. | | At present, our imagination is blocked by our egocentric vision of the world, which persuades us that the humanity is the unique and extraordinary product of the intelligence, but the given time to the evolution is infinite.
The life needs time to reach the complexity, and it is the result of an adaptation pressure to the environment. This pressure engenders the fact that living cells are what they are at a moment: the result of millions of different random phenomena (meteorite impacts, global cataclysms) which modify the evolution road towards the complexity.
These phenomena are real contingencies that the chronology is almost impossible to reproduce. What makes say to certain astronomers that the life on Earth is unique. It is sure that it is unique seemingly, we will not discover the other men somewhere else, but the life seems to be strength, present in the Universe, as contingencies the contingency is the negation of the necessity. A proposition is the contingent if it is not necessary (she could be false). Situation where the state of a system is determined by the value of independent, even contradictory internal and external parameters. the strength of gravitation, the electromagnetic strength, the strong nuclear strength and the weak nuclear strength (see the article of the Big Bang). (see the article on the Big Bang). | |  Image: The proof of extraterrestrial life could happen in a minute or millions of years but life on Earth has more than a billion years before it. |
The intuition of Hubert Reeves | | | | |
"I will use an indirect argument is that the three windows: the small, medium and large. The small window opens on the size of atoms and molecules. Astronomers have identified across the universe the same atoms as those we have here.
There is no atom present in the space that is not here on Earth, and vice versa. The same molecules space - some important structures, up to 115 atoms - are no different molecules land.
The laws of atomic physics are the same everywhere. Nature is structured in the same way, whether in the most distant quasars or the carpet.
The large window opens, meanwhile, about the size of galaxies and stars, that is to say the visible universe. All these stars are similar. Certainly they are not identical, but their structures, their evolution are essentially the same. Again, nature is organized in the same way, since our Milky Way galaxy visible to the first. Remains through the window, that is to say ours, that of living organisms. | | It is a dimension that we can not see today outside the Earth. But if nature is structured in the same way in the small and large window, it is also plausible that it is structured the same way in through the window. Better: it would be surprising if the nature, having structured the same way at all scales, has left a void in the middle...
Those who do not believe in extraterrestrial life as an argument often put forward the Fermi paradox.
In 1950, the Italian physicist Enrico Fermi posed the following question: if there are living beings everywhere, and therefore of civilization has reached levels of technology superior to ours, how is it that these aliens are not coming to Earth? "
Credit: Occasional Sciences et Avenir N ° 158 May / June 2009 Image: Enrico Fermi: If aliens exist, he asked, where are they? | | 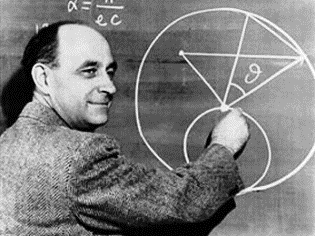 |
Kepler to search for exoplanets | | | | |
Kepler, the Space Telescope over a ton, went toward the Milky Way, March 6, 2009 at 22:48 hours in Florida, thanks to a Delta II rocket, the search for extrasolar planets or exoplanets.
The planets that Kepler telescope will search, the planets are small in size as Earth, they can not see that Corot. In March 2009, scientists say they have found 342 exoplanets, 289 stars with planets planets and 0 identical to the size of Earth.
The 342 planets are gas giants for the most part, but none in the habitable zone. It is to achieve this goal the Americans have launched the Kepler mission, designed to determine whether habitable planets outside our solar system.
Kepler will look closely for three and a half years, more than 100 000 stars in the Milky Way, rather in the regions of Cygnus and Lyra. It will detect planets orbiting stars similar to our Sun, rocky like our Earth and positioned more in the habitable zone, i.e. neither too far nor too near its star.
Kepler telescope features a specialized one meter in diameter with a field of vision of 105 degrees and an image resolution of 95 megapixels. | | This monster of Technology NASA sees broad as it is equipped with a photometer to measure the brightness of tens of thousands of stars simultaneously, to increase the chances of discovery by the transit method.
A transit occurs whenever a planet passes between its star and the observer, at that time, the planet obscures some of the light from the star, producing a detectable periodic dimming.
This signature is used to detect the planet and determine its size and orbit.
"The Kepler mission, for the first time, will allow humans to our galaxy to search for planets similar to Earth size or even smaller, " said principal investigator William Borucki Research Center of NASA, California. "
With its advanced capabilities, Kepler will help us answer one of the oldest questions in the history of man:
Are there other things that us, in the universe? " Image: the Kepler space telescope, over a ton, went toward the Milky Way, March 6, 2009. | |  |
More than a thousand planets Candidate | | | | |
The Kepler space telescope was launched by NASA in March 2009. Its mission is to find planets with characteristics similar to those on Earth.
Since the mission began in 2009, astronomers have discovered planets are 1235 candidates for life, revolving around distant stars.
Kepler's quest leads her into watching a very rich star field in order to detect transits of planets through the tiny drop in brightness that this mini-eclipse generates.
Using Kepler's third law, we deduce the period of revolution, the distance between the planet's sun.
This lets you know if the planet lies in the habitable zone of its star, neither too near nor too far.
On this spectacular illustration, we find the candidate planets Kepler telescope. Their shadows are represented at the same scale as their stars. Image: Kepler Space Telescope has discovered exoplanets 1235 since 2009. Many stars have more than one planet, but we must look at the image at high resolution to distinguish them. By comparison, the Sun is presented only to the same scale, and right below the first row, with transit Jupiter and Earth.
Illustration Credit: Jason Rowe, Kepler Mission. | | 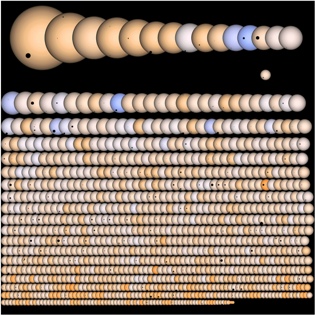 | |  Image: Representation of the Sun with the Earth and Jupiter. |
 Automatic translation
Automatic translation

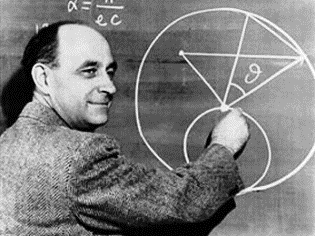






 Artificial intelligence: the explosion of gigantism
Artificial intelligence: the explosion of gigantism
 When AI models train on their own data, they go mad!
When AI models train on their own data, they go mad!
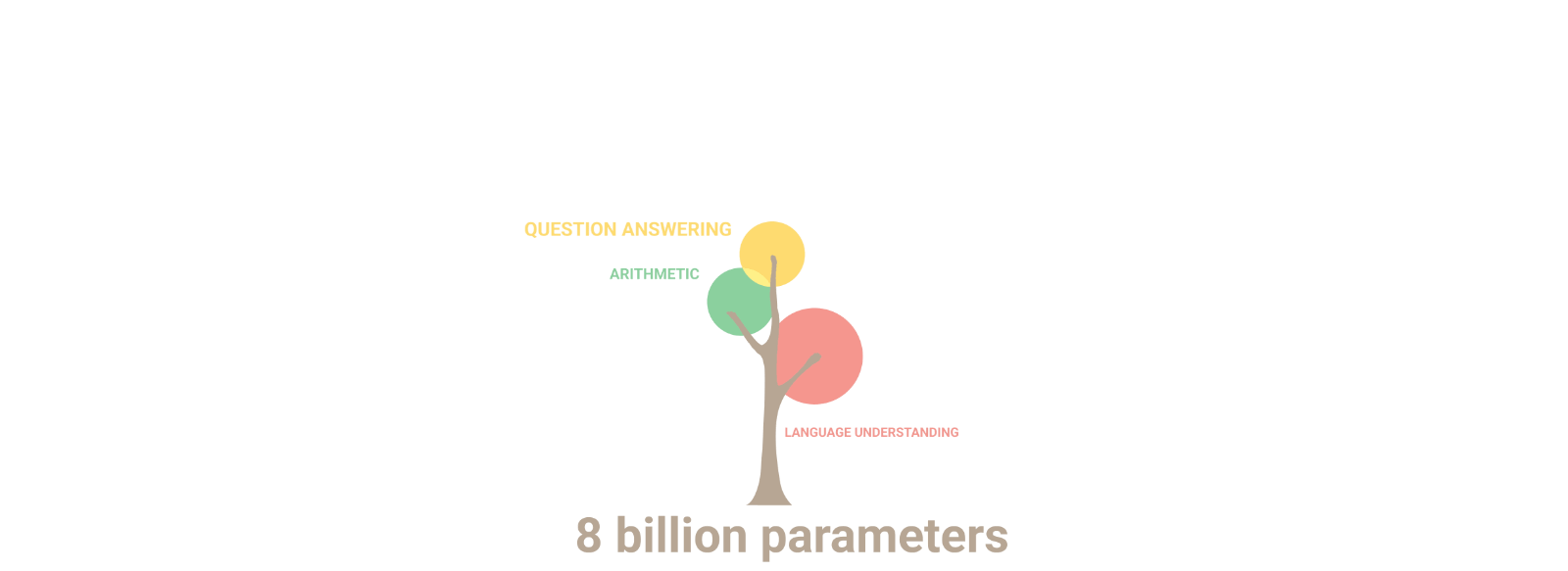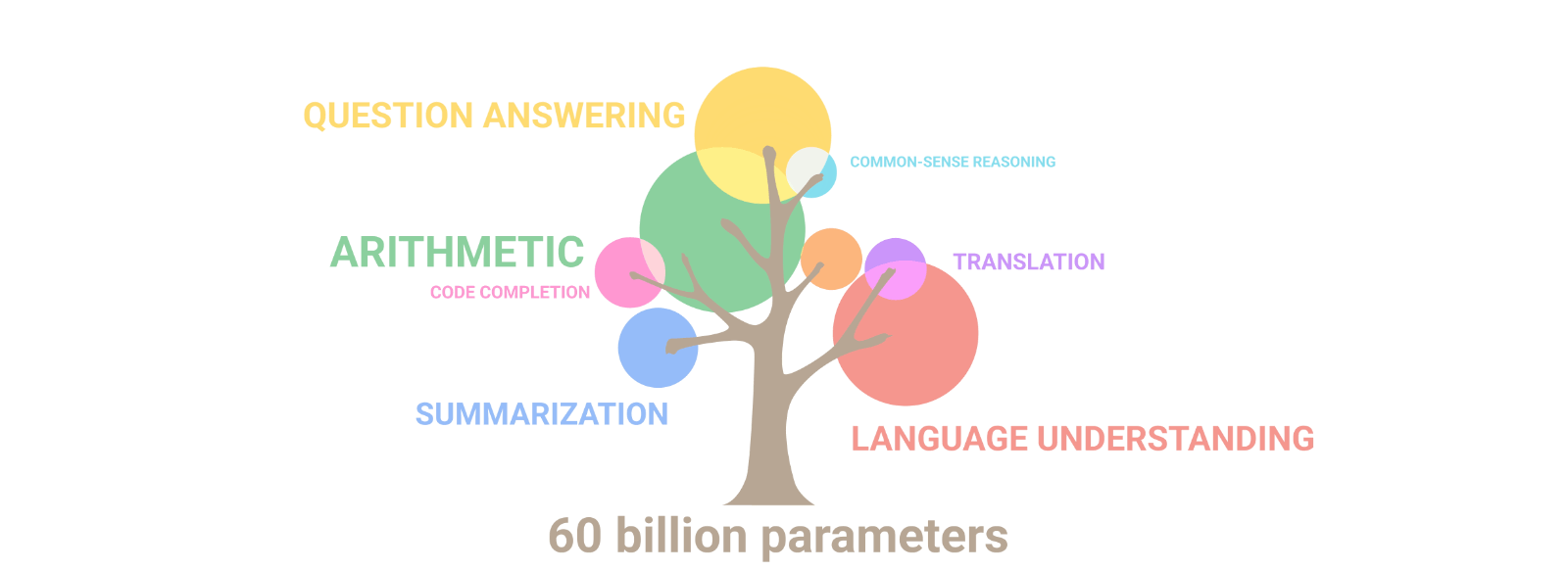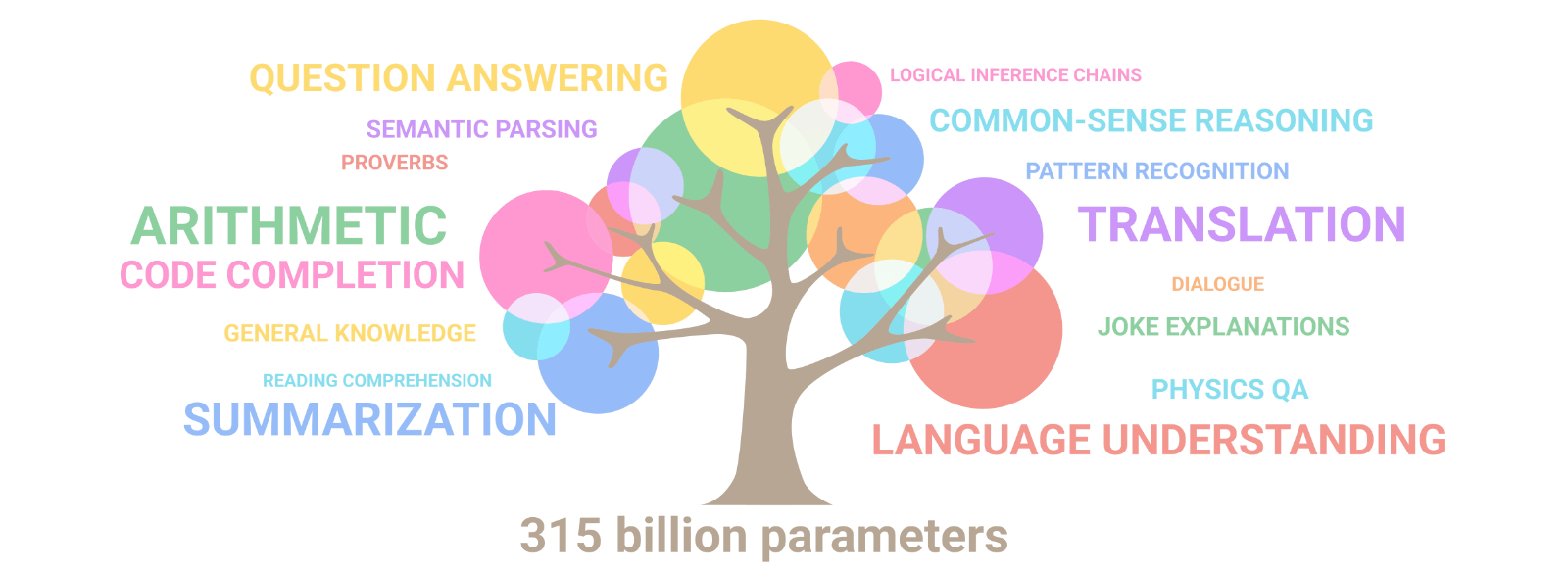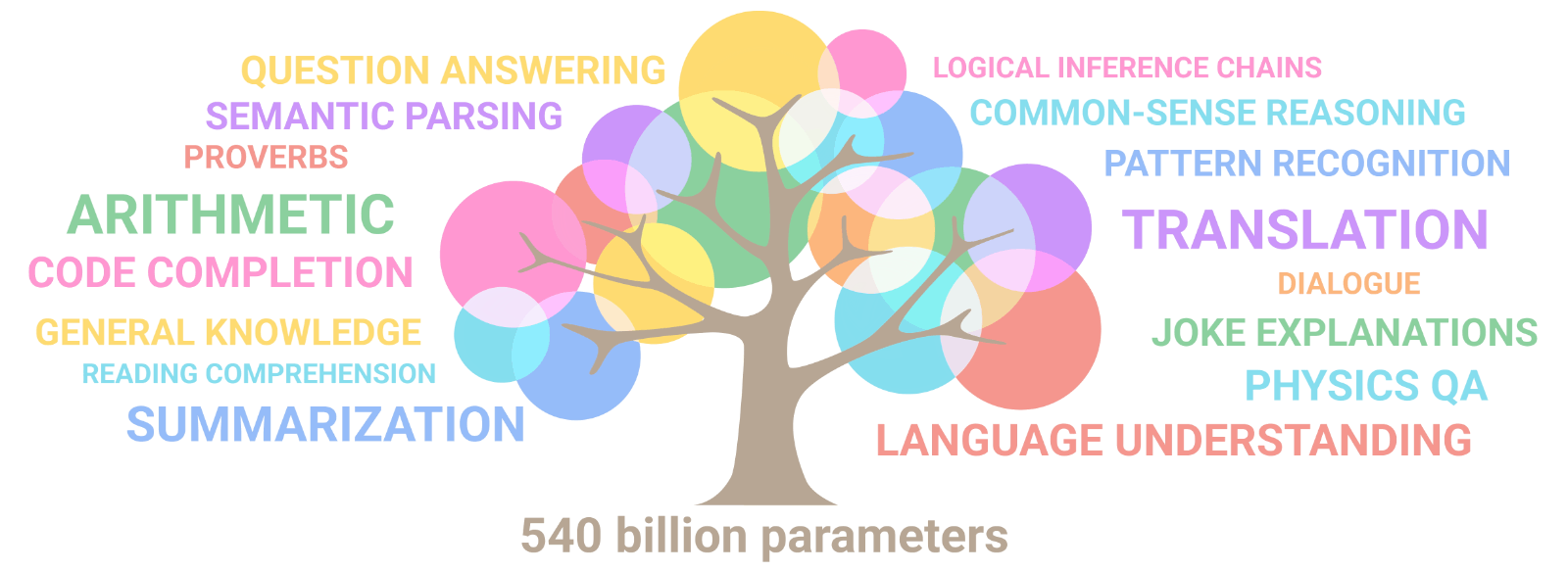 Emergence of artificial intelligence: Illusion of intelligence or intelligence?
Emergence of artificial intelligence: Illusion of intelligence or intelligence?
 The horseshoe crab, a living fossil!
The horseshoe crab, a living fossil!
 Biosignatures or presence of life in the Universe
Biosignatures or presence of life in the Universe
 Challenge and threat of Artificial Intelligence
Challenge and threat of Artificial Intelligence
 How do machines understand, interpret and generate language in a similar way to humans?
How do machines understand, interpret and generate language in a similar way to humans?
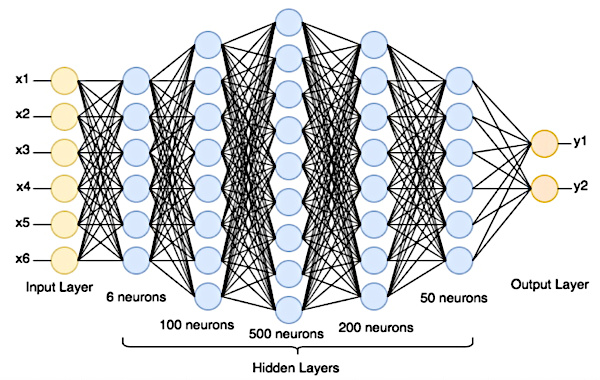 How does an artificial neural network work?
How does an artificial neural network work?
 Origin of life on Earth: Panspermia theory
Origin of life on Earth: Panspermia theory
 Origin of life on Earth: White smoker theory
Origin of life on Earth: White smoker theory
 Why 37 degrees Celsius?
Why 37 degrees Celsius?
 Thermodynamics of the sandpile
Thermodynamics of the sandpile
 Are we alone in the universe?
Are we alone in the universe?
 Trace of frozen life in Siberia
Trace of frozen life in Siberia
 Ice cores tell us about our past
Ice cores tell us about our past
 Life evolves in the shelter of glaciations
Life evolves in the shelter of glaciations
 Organ regeneration, the salamander
Organ regeneration, the salamander
 Cosmic rays and the mutation of species
Cosmic rays and the mutation of species
 Mephisto, the little worm of the depths
Mephisto, the little worm of the depths
 Discovery of solid buckyballs in space
Discovery of solid buckyballs in space
 Bipedalism in hominids
Bipedalism in hominids
 Kamchatka giant crab
Kamchatka giant crab
 The passage between the inert and the living
The passage between the inert and the living
 From particles to biochemical life
From particles to biochemical life
 Egocentric vision, the man at the center
Egocentric vision, the man at the center
 Megapod uses volcanic heat
Megapod uses volcanic heat
 Ardi is 4.4 million years old
Ardi is 4.4 million years old
 Natural selection, the birch moth
Natural selection, the birch moth
 The explosion of life in the Ordovician
The explosion of life in the Ordovician
 Liquid water, an accelerator of chemical reactions
Liquid water, an accelerator of chemical reactions
 Neandertal
Neandertal
 Asimo the future humanoid
Asimo the future humanoid
 Conditions for the appearance of life
Conditions for the appearance of life
 Fermi's paradox or Plato's cave
Fermi's paradox or Plato's cave
 The Tardigrade, the immortal animal
The Tardigrade, the immortal animal
 Toumaï, 7 million years old
Toumaï, 7 million years old
 Border between inanimate and living
Border between inanimate and living
 The incredible life of the abyss
The incredible life of the abyss
 Cyanobacteria create toxic gas
Cyanobacteria create toxic gas
 The short history of the evolution of life
The short history of the evolution of life
 The smallest frog in the world
The smallest frog in the world
 The explanation of the Little Ice Age
The explanation of the Little Ice Age
 Ashen light, the proofs of life
Ashen light, the proofs of life
 Bioluminescence of living organisms
Bioluminescence of living organisms
 Beyond our senses, the great scientific revolutions
Beyond our senses, the great scientific revolutions
 The primitive soup
The primitive soup